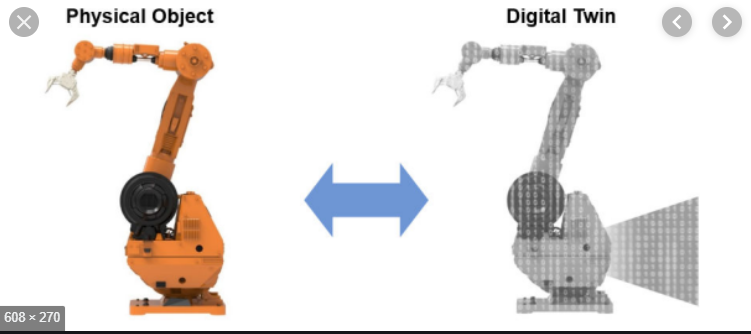
A digital twin can be defined, fundamentally, as an evolving digital profile of the historical and current behavior of a physical object or process that helps optimize business performance.
Throughout the product development life cycle, right from the design phase to the deployment phase, organizations can have a complete digital foot print of their products. These ‘connected digital things’ generate data in real time, and this helps businesses in better analyze and predict the problems in advance or give early warnings, prevent downtime, develop new opportunities and even plan better products for the future at lower costs by using simulations.
All these will have a greater impact on delivering a better customer experience in business as well.
Digital Twins which incorporates Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Internet of Things are key in Industry 4.0 and are predominantly used in the Industrial Internet of Things, engineering, and manufacturing business space. The widespread reach and usage of the Internet of Things have made the Digital Twins more cost-effective and accessible for the business world.
3 key areas
- Improvement in the manufacturing process.
- Provide efficient predictive maintenance of existing products.
- Developing new products based on real world usage of existing system.
How does a digital twin work?
- Digital Twins, the virtual counterparts of the physical assets are created as digitized duplicates of machines/ equipment or physical sites using sensors.
- These digital assets can be created even before an asset is built physically.
- To create a digital twin of any physical asset, the engineers collect and synthesize data from various sources including physical data, manufacturing data, operational data and insights from analytics software. All this information along with AI algorithms is integrated into a physics-based virtual model and by applying Analytics into these models we get the relevant insights regarding the physical asset.
- The consistent flow of data helps in getting the best possible analysis and insights regarding the asset which helps in optimizing the business outcome. Thus the digital twin will act as a live model of the physical equipment.
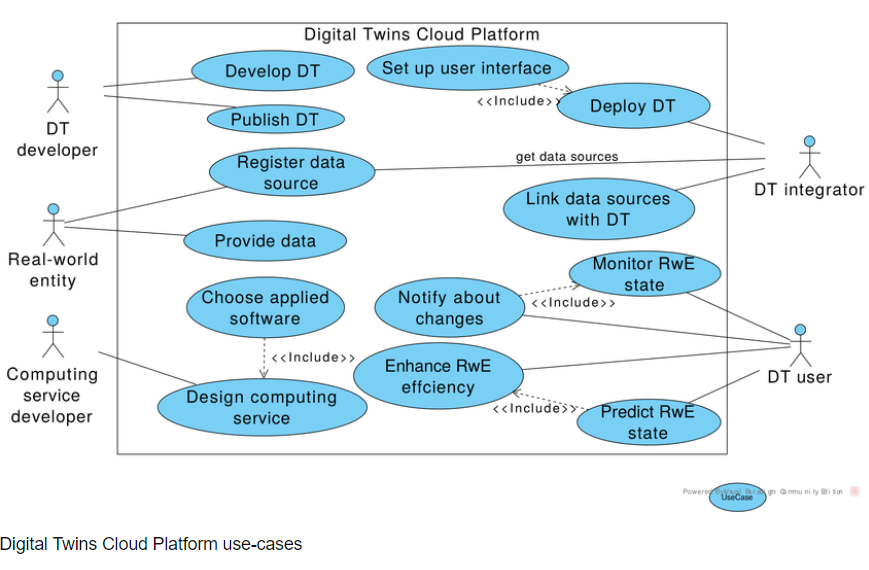
Digital Twin cloud platform
Providers
Siemens and Bentley Systems announce Plant Sight digital twin cloud services
Applications of Digital Twins
- Manufacturing
- Automobile
- Retail
- Healthcare
- Smart Cities
- Industrial IoT
save millions of dollars in maintenance costs and reduce product defects and shorten time to market.
Digital twins and IoT
digital twin enables a device-as-a-service.
Microsoft Azure IoT does have the concept of a ‘device twin’ that is part of their device management solution.
Amazon refers to a ‘device shadow’ as their version of a digital twin.
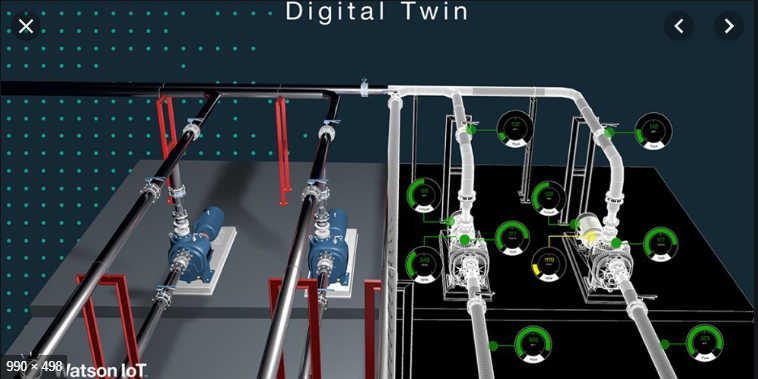
digital twin on IBM Watson IoT.
Digital twin vs. predictive twin
November 2017 article for Network World, contributor Deepak Puri outlined an example of an Oracle digital-twin tool that provides users with two options – a digital twin and a predictive twin.
The digital twin “can include a description of the devices, a 3D rendering and details on all the sensors in the device. It continuously generates sensor readings that simulate real life options.”
The predictive twin “models the future state and behavior of the device,”
Digital twins in the industry 4.0
Digital Twins is at the core of this new industrial revolution bringing an unlimited possibilities
It changes the traditional approach of ‘the first build and then tweak’ in the industrial world and brings in a more virtual system based design process that brings in the much more efficient role out of any equipment or system by understanding its unique features, performance, and potential issues if any.
Skills?
specialized expertise in machine learning, artificial intelligence, predictive analytics and other data-science capabilities.









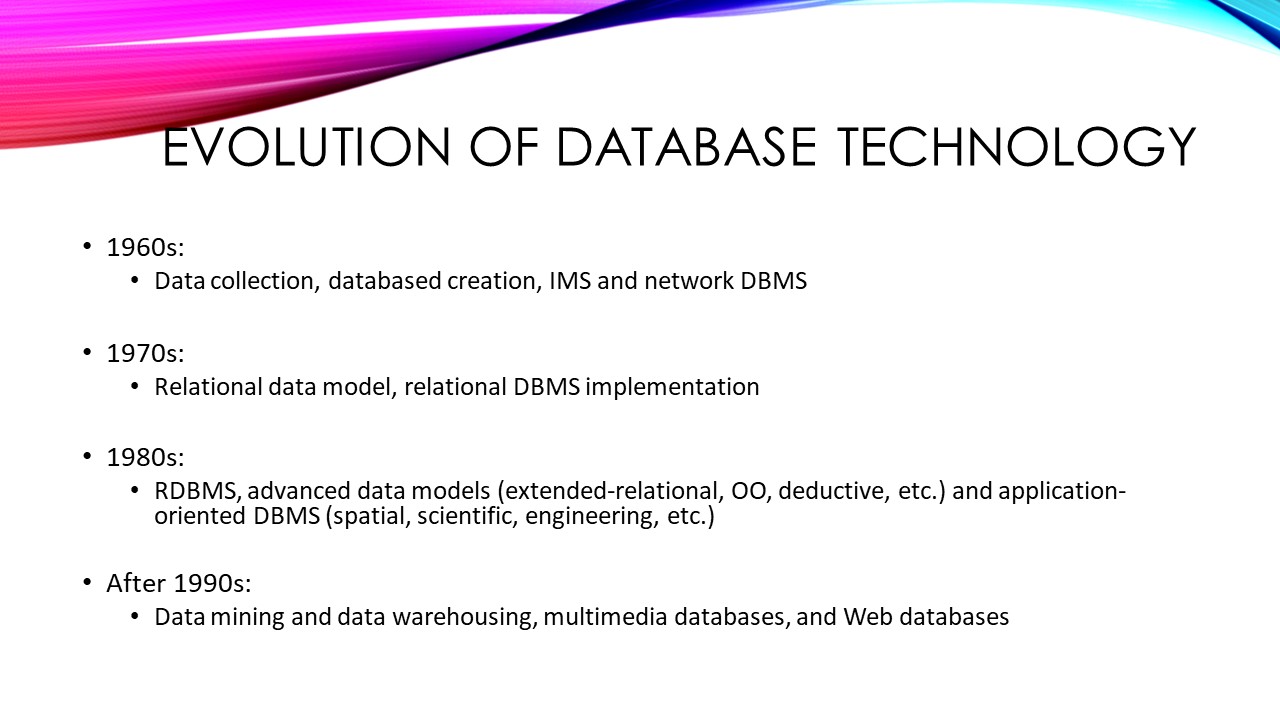
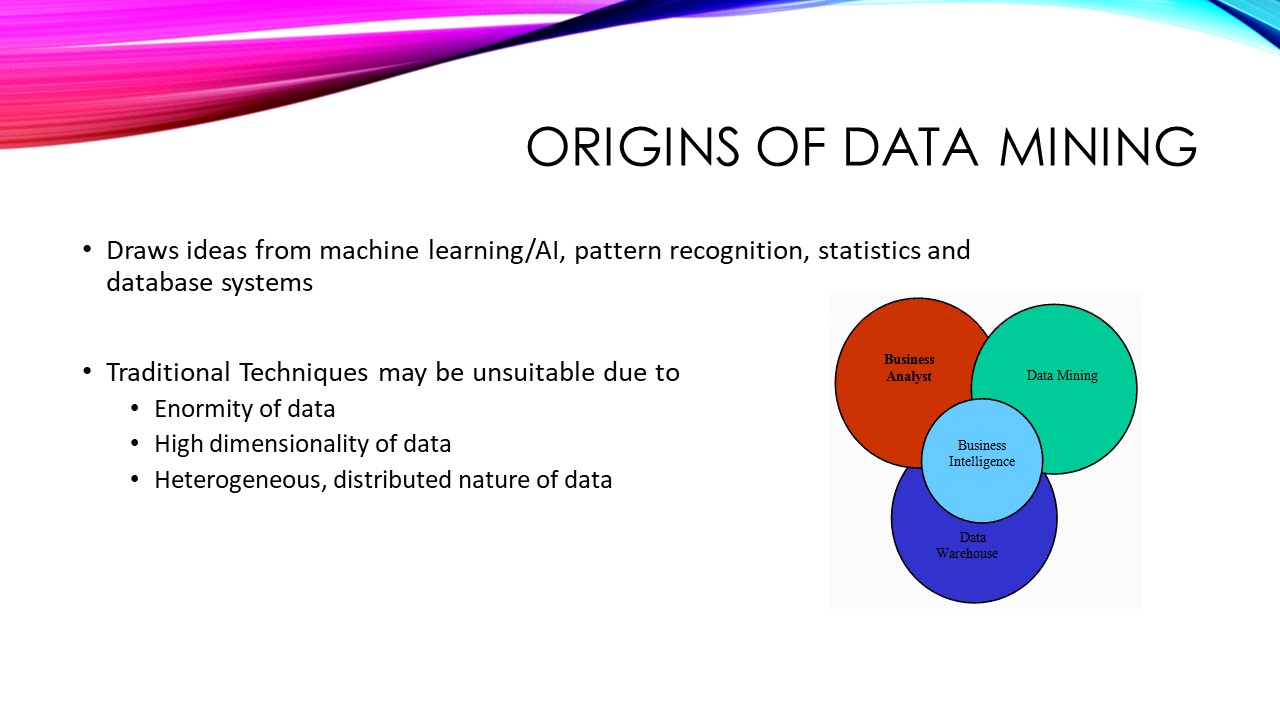




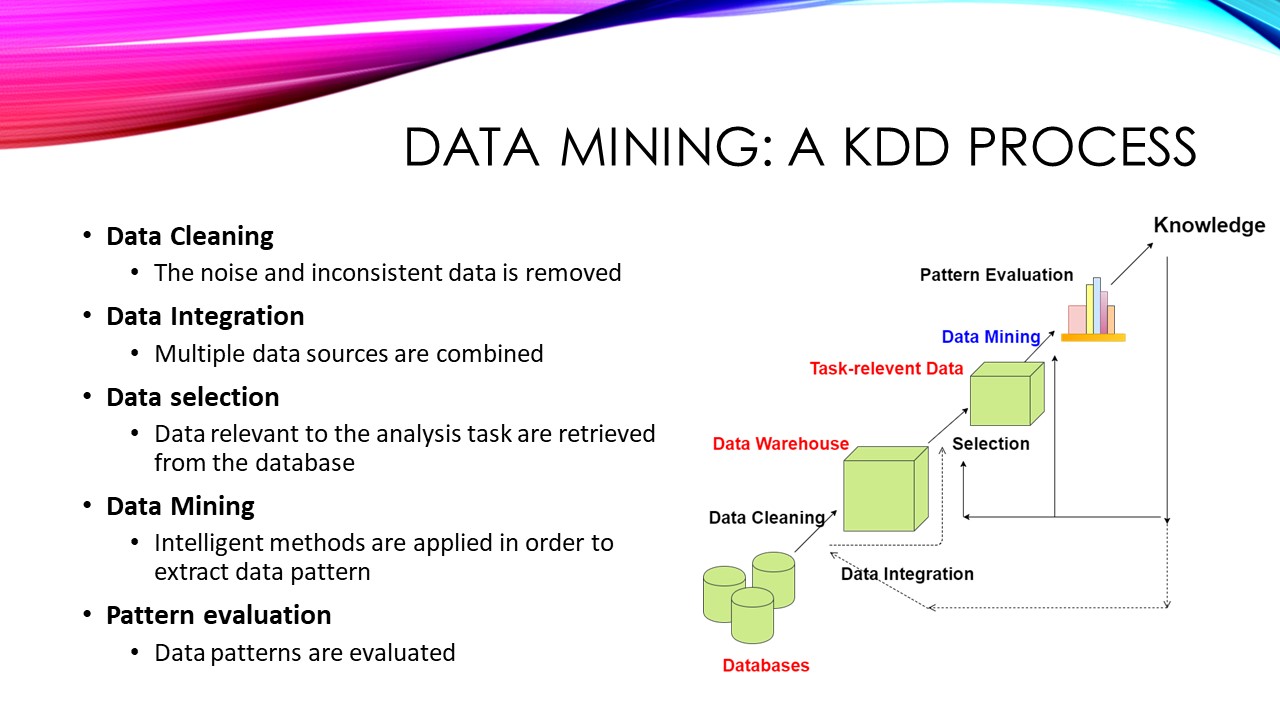

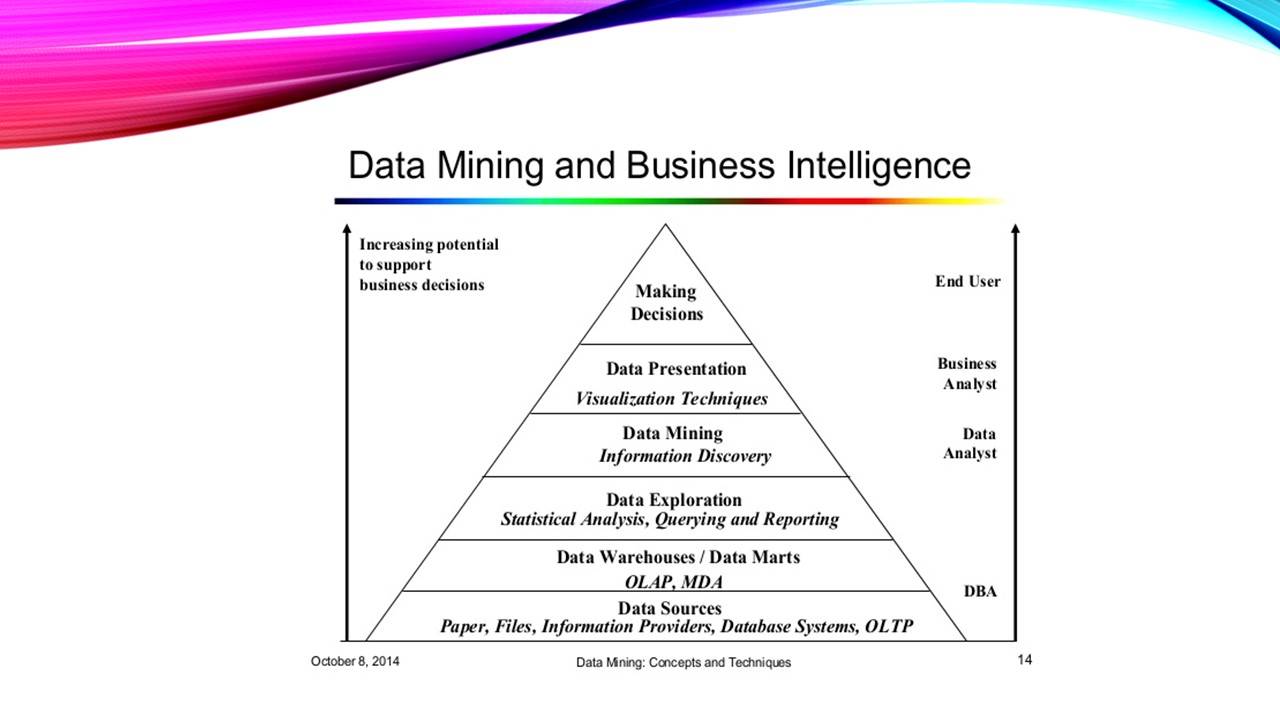


























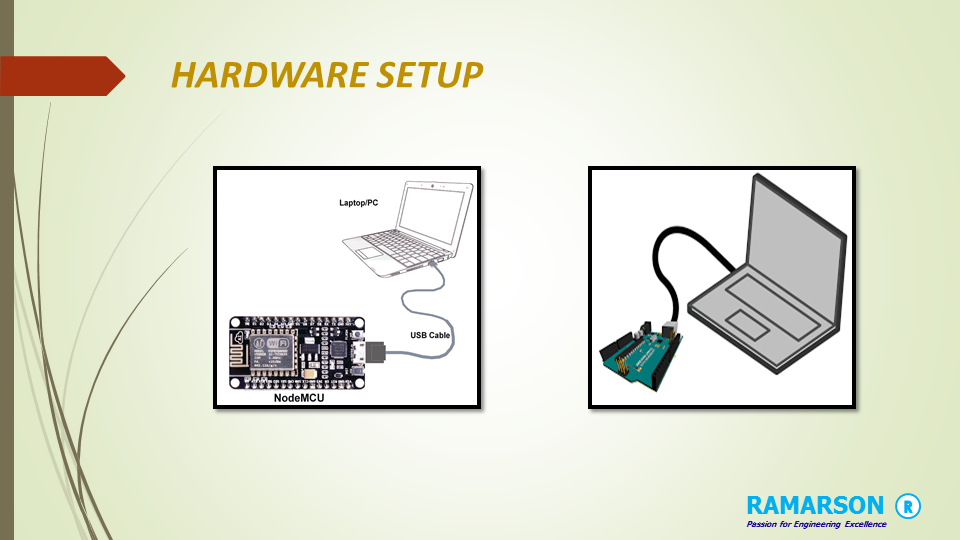
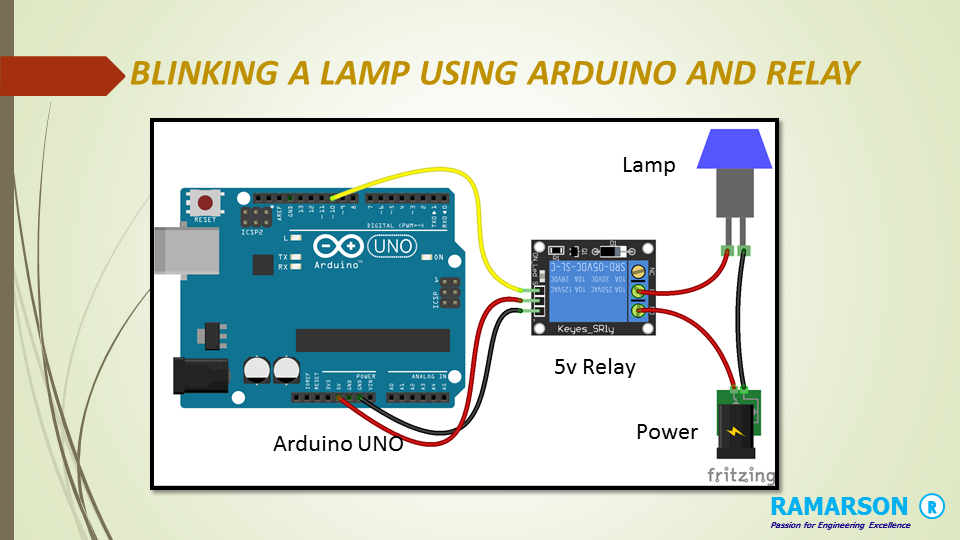



































 Using middleware in Golang is very simple, we have to use middleware between a ServeMux and application handlers. The Http Middleware function accepts a handler as a parameter and returns a handler so that we can directly register the Middleware function with the ServeMux.
Using middleware in Golang is very simple, we have to use middleware between a ServeMux and application handlers. The Http Middleware function accepts a handler as a parameter and returns a handler so that we can directly register the Middleware function with the ServeMux.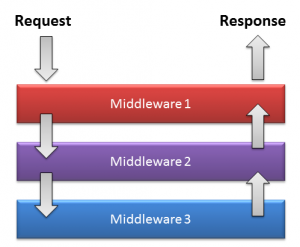 In Golang, we can create handler chain by nested middleware functions inside another function. We can share values and also pass errors from one handler to another using middleware chaining.
In Golang, we can create handler chain by nested middleware functions inside another function. We can share values and also pass errors from one handler to another using middleware chaining.
