By Vijayalakshmi Rajarajan-Senior Software Developer From Ramarson Technology Developers LLP
What is Augmented Reality ??
- The interactive experience of a real-world environment
- See the direct or indirect views of physical real-world environments
- Augmented with superimposed computer-generated images
- over a user’s view of the real world, thus enhancing one’s the current Opinion of reality.
- Used to add or enhance something on real things
- Graphics, sounds, and touch feedback are added into
- our natural world to create an enhanced user
experience
INVENTION OF AR SYSTEM
- In 1968 -The Sword of Damocles-ØIvan Sutherland invented the first VR head-mounted display at Harvard University.
- In 1975 -Videoplace-ØMyron Kruegercreated an artificial reality laboratory. The scientist envisioned the interaction with digital stuff by human movements
- In 1980s –EyeTap-ØSteve Mann formulated the concept ofmediated reality (first portable computer) , by using cameras, processors, and display systems
- In 1992 -Virtual Fixtures System-ØFirst functional AR system developed by Louis Rosenberg in U.S. Air Force
- In 2000 –ARToolKit-ØHirokazuKato(Japanese scientist) developed and published –an open-source SDK. Later it was adjusted to work with Adobe.
- In 2004 -helmet-mounted AR system-Trimble Navigation presented an outdoor .
- In 2008 -AR Travel Guide-Wikitude made map for Android mobile devices.
- In 2013 -Google Glass-Google beta tested this –with internet connection via Bluetooth.
- In 2015 Windows Holographic and HoloLens-Microsoft presented two brand new technologies: with an AR goggles with lots of sensors to display HD holograms
- In 2016 Pokemon Go game-Niantic launched this for mobile devices. The app blew the gaming industry up and earned $2 million in a just first week.
TYPES OF AUGMENTED REALITY
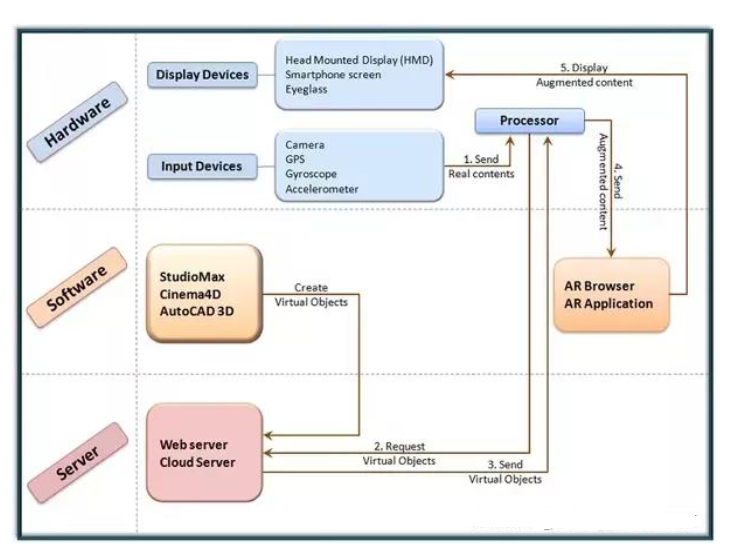
- Marker BasedAR-Also called as Image Recognition,Uses a camera and some type of visual marker [QR /2D Code]
- Marker-lessAR-Also called location-based, position-based Application
Uses a GPS, digital compass, velocity meter, or accelerometer which is embedded in the device to provide data based on your locationExample: Google Maps
- Projection BasedAR-Works by projecting artificial light onto real world surfaces.Allow for human interaction by sending light onto a real world surface and then sensing the human interaction (i.e. touch) of that projected lightExample : (3D) interactive hologram into mid-air.
- Superimposition BasedAR-Either partially or fully replaces the original view of an object with a newly enhanced view of that same object.object recognition plays a main role
Example :Ikea augmented reality furniture catalogue
Education: interactive models for learning and training purposes, from mathematics to chemistry.
- Medicine/healthcare: to help diagnose, monitor, train, localize, etc.
- Military: for advanced navigation, marking objects in real time.
- Art / installations / visual arts / music.
- Tourism: data on destinations, sightseeing objects, navigation, and directions.
- Broadcasting: enhancing live events and event streaming by overlaying content.
- Industrial design: to visualize, calculate or model.
DISADVANTAGES TO BE NOTED FOR AR
- Information overload
- Perception impairment
- Distraction
- Privacy
- Security